Choosing the Right Laser Welding Machine
2025-05-24

Choosing the right laser welding machine is crucial and will significantly affect the quality, efficiency and cost-effectiveness of welding operations. Whether you are engaged in metal processing, automotive manufacturing, medical device production or aerospace, the right laser welding machine can provide precision, speed and strength that traditional welding methods cannot match.
However, there are many types of fiber laser welding machines on the market, with different power levels and functions. How to choose the most suitable metal laser welding machine according to specific needs?
Aorelaser will introduce you to how to choose the ideal laser welding machine, including types, main functions, application scenarios and expert advice to help you make the right decision.
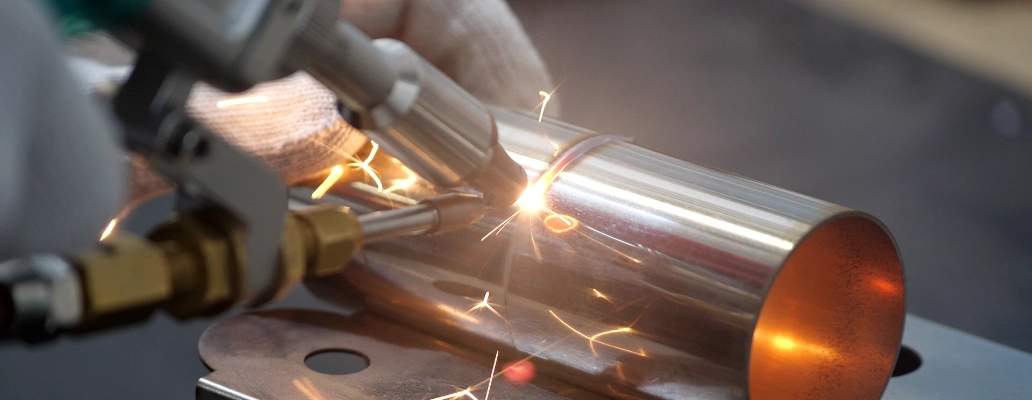

How to choose a laser welding machine
First, we need to understand what a metal laser cutting machine is, the differences and advantages of fiber laser welding machine over traditional welding methods; second, we need to understand the precautions for selecting a laser welding machine; finally, choose a machine that suits you according to your needs and budget
What is a fiber laser welding machine?
Laser welding machines use a focused beam (laser) to connect materials (usually metals or thermoplastics) with high precision and minimal thermal deformation. The laser beam melts the material at the joint to form a strong, clean weld.
Unlike traditional welding methods, metal laser welding has the following advantages:
High precision: suitable for welding precision parts (such as electronic components, medical devices).
Fast speed: 3-5 times more efficient than traditional welding, reducing production costs.
Strong adaptability: can weld a variety of metals such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper, titanium, etc.
Low thermal impact: reduce material deformation and improve yield rate.
Common welding machines:
1. Arc welding machine
Use arc to melt metal at high temperature. Common types:
Manual arc welding (MMA): flexible operation, low cost, but dependent on worker skills.
MIG/MAG welding:
MIG welding: suitable for aluminum and stainless steel. MAG (active gas): suitable for carbon steel.
TIG welding: high precision, no spatter, used for thin plate and pipe welding.
Advantages: low equipment cost and strong adaptability.
Limitations: large heat-affected zone and high risk of deformation.
2. Fiber Laser welding machine
High-energy laser beam melts materials to achieve precision welding. Fiber laser welding machine has high beam quality and is suitable for precision metal welding (mainstream choice).
Advantages: fast speed, high precision and small thermal deformation.
Limitations: high equipment cost and strict requirements on assembly accuracy.
3. Spot welding/seam welding
The current passes through the metal contact surface to generate resistance heat and pressurize the welding.
Application: welding of automobile body and battery tab.
Advantages: No welding materials are required, and the efficiency is extremely high.
Limitations: Only suitable for conductive materials, and the workpieces need to be in close contact.
4. Plasma arc welding machine
Principle: Compressed arc forms high-temperature plasma with strong penetrating power.
Application: Thick plate stainless steel, titanium alloy welding (such as chemical containers).
Advantages: Large weld depth-to-width ratio, single-sided welding and double-sided forming.
Limitations: Complex equipment, requiring professional operators.

Things to know before buying a metal laser welding machine
Before buying a metal laser welding machine, there are several important factors to consider.
Power output: Evaluate the power output of the machine, as it determines the welding speed and strength. Higher power outputs allow for faster and stronger welds, while lower power may be more suitable for welding delicate materials.
Low power (<1000W)fiber laser welder: Suitable for precision welding of thin plates (0.1-2mm), electronic components, etc.
Medium power (1000-1500W) metal laser welding machine: General purpose, suitable for automotive parts and home appliance housings.
High power (>1500W)laser welding machine: Thick plates (>5mm), heavy industrial welding.
Tips: The higher the power, the higher the cost, which needs to be matched according to the material thickness.
Welding materials and industry needs:
Stainless steel/carbon steel: General-purpose equipment can cover it.
Aluminum alloy/copper: You need to choose a model equipped with the "high-frequency modulation" function to prevent reflection from burning optical components.
Industry case:
Automotive industry: Recommend models with the "swing welding" function to improve weld strength.
Pulse Frequency: Consider the pulse frequency options available on the laser welder. Different frequencies are suitable for different materials and welding applications.
Spot Size Range: Evaluate the spot size range available on the machine. This determines the precision and accuracy of the weld. Make sure it meets your project requirements.
Cooling System Requirements: Check the cooling system requirements of the laser welder. Efficient cooling is essential to prevent overheating from prolonged use.
Weld Quality: Consider whether the machine can achieve the welding quality standards you expect. Some machines have greater precision and control than others, resulting in higher quality welds.
Certifications & Compliance: Check if there are certificates such as CE certification, FDA certification, etc.
Training and Technical Support: Make sure that appropriate training is provided to effectively operate and maintain the laser welder. Technical support should also be provided if any problems arise during use.
About Aore Laser
The main products include laser cutting machines, laser welding machines, laser cleaning machines, etc. It has professional service personnel in English, Spanish, Korean, Portuguese, and other languages, providing on-site installation training services and 24-hour online services.




